1

(Summary description)Cervical cancer is a common malignant tumor of female reproductive system. Its appearance is actually closely related to women’s diet and living habits. If you don’t pay attention in your life, it is very easy to cause lesions and lead to the appearance of various uterine diseases. Then how does cervical cancer form step by step? It may have these characteristics. Women will be welcomed by cervical cancer, we better not ignore it.
(Summary description)Cervical cancer is a common malignant tumor of female reproductive system. Its appearance is actually closely related to women’s diet and living habits. If you don’t pay attention in your life, it is very easy to cause lesions and lead to the appearance of various uterine diseases. Then how does cervical cancer form step by step? It may have these characteristics. Women will be welcomed by cervical cancer, we better not ignore it.
Cervical cancer is a common malignant tumor of female reproductive system. Its appearance is actually closely related to women’s diet and living habits. If you don’t pay attention in your life, it is very easy to cause lesions and lead to the appearance of various uterine diseases. Then how does cervical cancer form step by step? It may have these characteristics. Women will be welcomed by cervical cancer, we better not ignore it.
The picture shows the HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) cervical cycle, showing the development process from normal cervix to invasive cervical cancer. CIN stands for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. HPV infection is an important factor of cervical cancer, let's mainly talk about this.
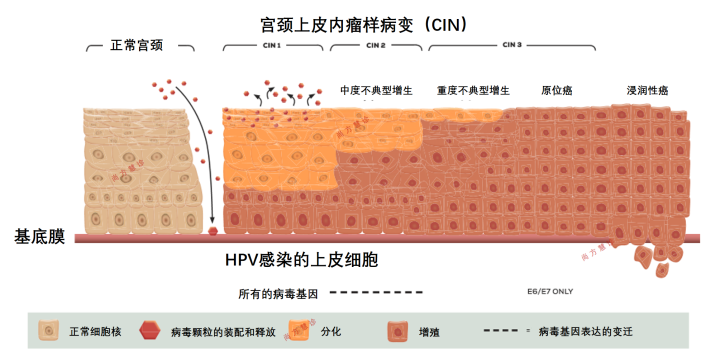
In layman's terms, this is a long-term process. Of course, in many countries, the age of first sexual intercourse is negatively correlated with the prevalence of cervical HPV; however, in some poor areas, HPV of all age groups The prevalence is very high. The incidence rate is a U-shaped curve. Most cervical HPV infections are asymptomatic, and 90% of detected infections cleared within 2 years, possibly due to cell-mediated immune mechanisms. However, persistent infection, combined smoking, low immunity, HIV infection, unbalanced diet, etc., will further increase the risk of cervical cancer. Most cervical HPV infections are asymptomatic, and 90% of detected infections cleared within 2 years, possibly due to cell-mediated immune mechanisms.
Cervical transformation process cancer:
In order to cause infection, human papillomavirus (HPV) and heparan sulfate proteoglycan combine on the basement membrane at the epithelial rupture (the arrow mark), resulting in infection of the basal epithelial cells. Uninfected epithelial cells are on the left, and HPV-infected epithelial cells are shown on the right. The viral genome is maintained as free DNA in the nucleus of the infected cell, and when the infected cell moves to the epithelial surface, the expression of viral genes changes. The later stages of the production cycle occur in the upper layers, and terminally differentiated epithelial layers and progenitor viruses are released from these upper layers (red hexagons). The expression of viruses E6 and E7 cancels the regulation of the cell cycle and pushes differentiated cells into S phase, so that the viral genome is amplified in cells that normally exit the cell cycle.
If left untreated, HPV infection that persists for decades can progress to cancer. As age increases, persistent cervical HPV infection is related to HR-HPV and multiple HPV infections. Smoking increases the risk of undesirable proliferation of cervical cancer and can increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma by three times. The state of low immune function also increases the risk of cervical lesions and the latent reactivation of genital HPV. Infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) makes the risk of HPV-related cervical cancer five times higher than the risk of no HIV infection. In addition, due to the increase in concurrent HIV infection, cervical dysplasia will progress to the risk of cancer. Invasive cervical cancer is now considered to be an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome disease. Reproductive factors, such as the combined use of estrogen and progesterone oral contraceptives; and other sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia and herpes simplex virus type 2, are now considered less closely related risk factors for cervical cancer.
In the cervix, a low folate state may increase the risk of cancer. In addition, the specific microbial distribution is associated with cervical CIN2 or higher-level CIN risk factors. It is recommended to combine feasible methods, including probiotics and vitamin supplementation, and vaccinations for cervical cancer to reduce the overall risk of cervical cancer.
Protective reproductive factors for cervical cancer, independent HPV status, including the use of intrauterine contraceptive devices, sexual intercourse with circumcised partners, and constant use of condoms. There is conflicting evidence about whether male circumcision prevents male infection with HPV, but some studies report that it is a protection. When a male partner uses a condom, the risk of female cervical HPV infection is reduced by 80%, while using a condom for 6 months can cause cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in women who have been infected to a higher than 20% clearance rate .
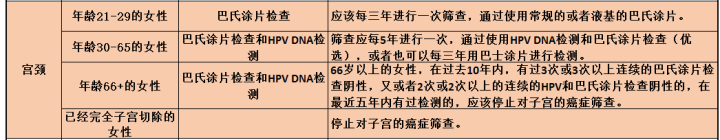
The methods of preventing or reducing risks and early screening are as follows:
①Use condoms
②Don’t have sex too early
③Quit smoking
④A balanced diet
⑤ Vaccination against cervical cancer
⑥ Reasonable screening.
Scan the QR code to read on your phone
related news
COPYRGIT @ 2021 en.new.hilans.cn All Rights Reserved Powered by www.300.cn | 鄂ICP备19028036号-1
Company Address: Middle Section of Chongli Road, Xiaohan Avenue, Xiaonan District, Xiaogan City
24-hour service hotline:13507170818 Service Hotline (TEL):86-0712-2369936 Contact QQ (working hours): 847453892

COPYRGIT @ 2021 en.new.hilans.cn All Rights Reserved Powered
by www.300.cn | 鄂ICP备19028036号-1
Company Address: Middle Section of Chongli Road, Xiaohan Avenue, Xiaonan District, Xiaogan City
24-hour service hotline:13507170818
Service Hotline (TEL):86-0712-2369936
Contact QQ (working hours): 847453892
